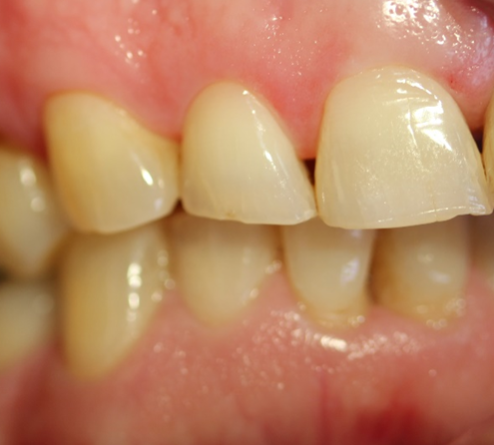
Enamel defects are disturbances in the quality and /or quantity of enamel. Enamel is one of the four components that make up a tooth. It covers the visible part of the tooth called the crown. Both the deciduous and permanent teeth can be affected by these defects.
What causes enamel disturbances?
There are a multitude of different things that can result in enamel defects; these include genetic factors, environmental factors such as trauma, prenatal or perinatal illness, vitamin deficiency, coeliac disease, and kidney disease.
What do they look like?
The enamel defects may be localised to one tooth or may affect multiple teeth. Teeth with enamel defects may have pits, tiny groves, depressions, and white spots or yellowish-brown stains. Defects may be localised to a small area of a tooth(demarcated) or can affect a lot of the tooth surface (diffuse).
Will Teeth be Symptomatic?
Teeth affected by enamel defects may experience more sensitivity to temperatures and sugary foods. The colour and size of the tooth may also be affected.
Enamel Defects and Tooth Decay
Teeth that have enamel defects are more susceptible to tooth decay, erosion, and premature tooth wear.
How Can I Prevent Enamel Defects?
Enamel defects cannot be prevented as they form when the tooth is developing in utero. However, you there are things you can do to reduce the risk of dental disease that may arise as a result of enamel defects. These include:
- Regular dental visits: Taking your child to visit their dentist at a young age can help identify the presence of enamel defects and other risk factors early. This allows the dentist to put in place preventative strategies for your child and provide appropriate treatment if required. Your dentist may recommend preventative treatments like fissure sealants, or topical fluoride. Sometimes the tooth may require restorative treatments like composite fillings (white fillings) or stainless-steel crowns.
- Oral Hygiene: Tooth decay and gum disease can be prevented by maintaining good oral hygiene. This involves brushing twice a day for 2-3 minutes with a toothpaste that contains fluoride. This helps to prevent cavities and will strengthen the tooth surface. It is also important to clean in between your teeth. There are lost of things available to help this such as dental floss, interdental brushes, and water flossers.
- Diet: Oral diseases like tooth decay require sugar to progress. By reducing the amount and frequency of sugar in your child’s diet, this can reduce the risk of tooth decay. This is particularly important if there are enamel defects present as the tooths natural protection(enamel) may be compromised.